Peripheral artery disease (PAD) might not be a household name, but it’s a surprisingly common condition affecting millions worldwide. This blog aims to shed light on PAD, its causes, symptoms, and most importantly, treatment options, including a minimally invasive procedure called interventional radiology (IR).
Understanding the Arterial Highway
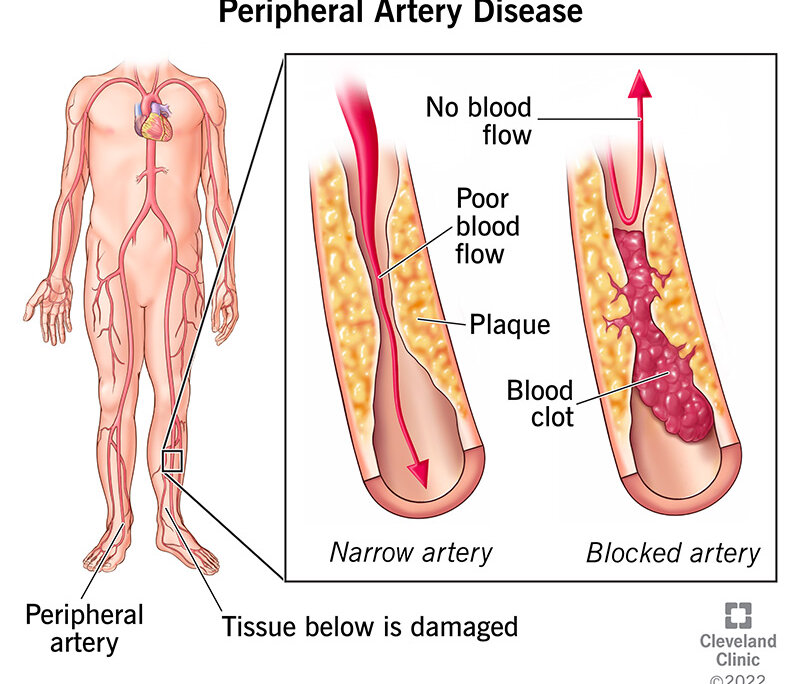
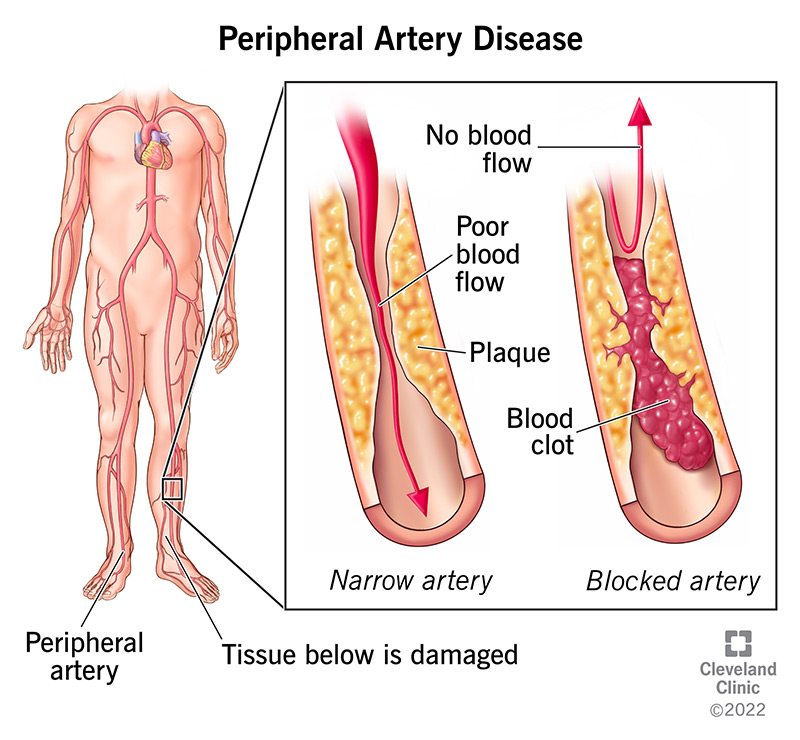
Imagine your body as a bustling city. Arteries are the highways that transport oxygen-rich blood, the lifeblood of your cells, throughout your body. PAD disrupts this vital flow, causing a narrowing of the arteries, typically in the legs and feet. This narrowing is often caused by a buildup of plaque, a sticky substance containing fat, cholesterol, and other elements.
The Silent Threat: PAD Symptoms
PAD can be a silent thief, progressing gradually without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease advances, you might experience:
- Claudication: This is the most common symptom, causing leg pain or cramping when walking or climbing stairs. The pain typically eases with rest.
- Rest pain: This pain occurs even when you’re not active, often at night, and might be described as a throbbing or burning sensation in the affected leg.
- Numbness or weakness: You might experience a feeling of numbness or weakness in the affected leg.
- Skin changes: PAD can cause the skin on your legs or feet to become pale, cool, or develop sores that heal poorly.
Risk Factors: Who’s More Susceptible?
Certain factors increase your risk of developing PAD, including:
- Smoking: This is the single biggest risk factor for PAD. Smoking damages the artery walls and accelerates plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, making it harder to detect PAD symptoms.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure puts additional stress on your arteries.
- High cholesterol: High levels of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol contribute to plaque formation.
- Family history: PAD can run in families.
- Age: The risk of PAD increases with age.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts a strain on your circulatory system.
Early Detection is Key
If you suspect PAD based on the above symptoms or have any of the risk factors, consult your doctor for a comprehensive evaluation. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and prevents complications. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, pulse checks in different parts of your legs, and an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test. This painless test compares blood pressure readings in your ankles to those in your arms.
Treatment Options: Taking Back Control
Fortunately, PAD is a manageable condition. While there’s no cure, various treatment options can improve blood flow, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. These include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, exercising regularly, and managing diabetes and high blood pressure are crucial.
- Medications: Medications can help lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, and manage pain.
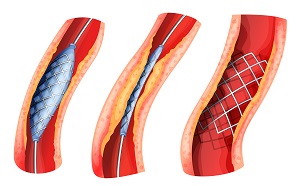
- Angioplasty: In this minimally invasive procedure, a tiny balloon is inserted into the narrowed artery and inflated to open it. A stent, a small mesh tube, might be placed to keep the artery open.
- Bypass surgery: In more severe cases, a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body is grafted to bypass the blocked artery.
Interventional Radiology (IR): A Revolutionary Approach
IR offers a minimally invasive and image-guided approach to treating PAD. IR specialists utilize advanced imaging techniques like X-rays, fluoroscopy, and ultrasound to access and treat narrowed arteries. Here are some IR techniques used for PAD:
- Angioplasty and stenting: Similar to the traditional procedure, but performed by IR specialists using a catheter inserted through a small incision in the groin or arm.
- Peripheral arterial embolization (PAE): This technique uses tiny particles to block bleeding vessels in the leg, promoting blood flow to healthy tissues.
Benefits of IR for PAD Treatment
IR offers several advantages over traditional surgery for PAD:
- Minimally invasive: Smaller incisions translate to less pain, faster recovery, and a shorter hospital stay.
- Image-guided precision: IR specialists have real-time visualization of the arteries, ensuring accurate treatment.
- Faster recovery: This allows patients to return to their regular activities quickly.